Why Become Board Certified?
ABMS board certification demonstrates to your patients, employers, and peers that you have made a commitment to:
- High professional standards, lifelong learning, and assessment
- Ongoing proficiency in competencies required of a physician or specialist
- Critically evaluating your practice
- Acquiring new skills
- Adapting your practice to changing patient health needs
As a physician or specialist who is board certified, you show:
To Patients and Families — that you care enough to be tested against rigorous standards and continue to learn and improve your practice.
- 98% of patients expect their doctors to stay up to date with the latest medical advances
- Patients often seek information about their doctor’s board certification through ABMS Certification Matters
To Employers — that you are valuable in supporting an environment of professionalism.
- Many organizations require board certification as a condition of employment
- Commitment to board certification contributes to staff retention and increased patient safety
To Colleagues — that you are a role model for:
- Professional development
- Lifelong learning
- Dedication to excellence in patient care
How Do I Get Board Certified?
How does the board certification process work? Most physicians and specialists follow this step-by-step approach.
- MEDICAL SCHOOL
Complete a post-graduate degree in medicine, achieving either a medical doctor or doctor of osteopathy degree. - LICENSURE
After completing medical school, you must pass the United States Medical Licensing Examination to receive a license to practice medicine in a particular state. - RESIDENCY
Following medical training, you can identify yourself as board eligible. You have three to seven years, depending on the ABMS Member Board requirement, to take a specialty certification exam. All training and other requirements defined by the ABMS Member Board must be met before taking the exam in a specialty or subspecialty. Learn about the specialties and subspecialties where board certification is offered. - CERTIFICATION EXAMINATION
During the final year of residency, you may apply for board certification examination. The exam is generally computer-based. Some boards give two exams: one general, another specialty specific. A separate oral examination may be required. - BOARD CERTIFICATION
Once you successfully pass the examinations, you are certified in your specialty. This is the first step in setting yourself apart as a board certified specialist. - SUBSPECIALTY EXAM AND CERTIFICATION
After becoming board certified in a specialty, if you are interested in a specific area of a specialty, consider subspecialty certification. You can usually take the exam after completing fellowship and meeting the eligibility criteria. Successful completion of the examination means you are now board certified in that subspecialty. - CONTINUING CERTIFICATION
Becoming board certified is just the beginning. After demonstrating that you meet the competency standard, you commit to keeping your medical knowledge current, your skills sharp, and your quality improving. The ABMS Member Board’s continuing certification programs provide a framework and tools to do so.
What Are the Requirements for Certification?
Contact the ABMS Member Board for the specialty you are interested in to learn more about certification requirements.
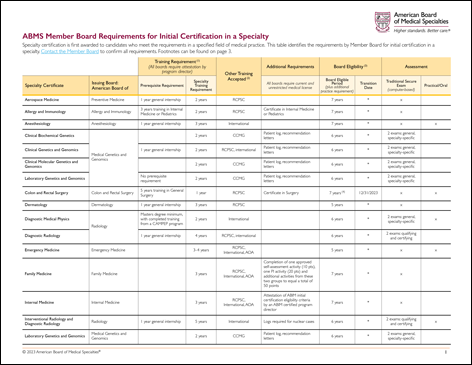
See the basic requirements for specialty certification by an ABMS Member Board.
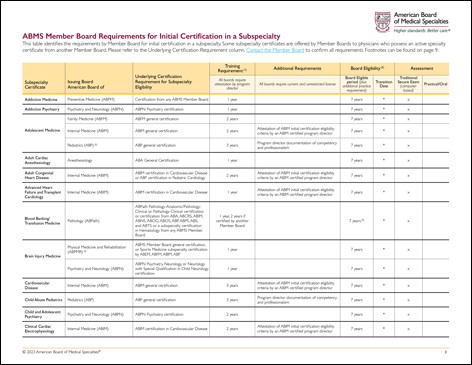
See the basic requirements for subspecialty certification by an ABMS Member Board.
